A new way to approach your PPC personas: Learning from the sales process to limit waste and accelerate ROI
By splitting your personas into buyer types, you’ll have more targeted messaging and higher conversions.
Learning from the sales process: An introduction to buyer influencers
These buyer personas are based on a book called, The New Strategic Selling by Robert B. Miller and Stephen E. Heiman. “Your strategy can only begin when you know who your players are,” added Farley. “The best way to think of it is like a football team: every player must be on the field to close the deal.”
- Economic buyer. Has the ability to commit funds to a purchase
- User buyer. The end-user of your product or service
- Technical buyer. Ensures all the technical specifications are met
- Coach. Really wants your solution to win
When we take this into our marketing efforts, we need to understand what each audience cares about most, what their content preferences are, and what channels they’re most likely to engage in.
Economic buyer

“This person prefers content with data visualizations, photography, and charts because they’re ROI-focused and need the social proof behind any decision that they’re going to make,” said Farley. They’re also high consumers of video content and love to see case studies and financial models.
User buyer

The user buyer is the one responsible for screening out potential solutions and understands all the key factors that go into various options they’re considering. This person is interested more in the details than the high-level overview that the economic buyer might find more interesting. The user buyer engages with charts, infographics, solution comparison guides, or category matrices.
“They’re whole ‘thing’ is being able to pitch [the product/service] to their economic and technical buyers,” added Farley. This user also cares deeply about how the solution will help them: will it make my job easier, better, faster, etc.?
Technical buyers

This buyer’s main role is to run interference for the economic buyer. “At the enterprise level, we see this with purchasing departments or procurement, but it can also be an operations manager. The question this buyer is always asking if the solution has what it takes to make the entire organization successful. The technical buyer is focused on data and leverages the user buyer for expertise.
Coach

This can be any of the other buyers or an outside influencer. They have potential personal gain from you winning. “This is someone who’s going to get something from your solution being the key decision,” said Farley. If you have a key influencer in your audience who is also a coach, that’s how to unlock success from marketing campaigns.
How to leverage these buyer personas in your PPC campaigns
Step 1. Define the buyer influencers. This is the part where you amass as much information as you can. Talk to customer service, sales teams, marketing teams, and more. Determine the person’s role in the buying process, their background and education, the company size, the buyer’s demographics or other defining traits, and their motivations, pain points and entry points.
“If they’re in growth mode, that’s a good foot in the door. But if they’re in trouble, it will always trump growth in sales,” said Farley. “So, from a marketing perspective, if we know trouble pain points, that’s also where we should focus because we know that it will ultimately make the difference.”
Step 2. Perform audience research. Now that you’ve found each buyer type and maybe new ways to think about your audience, you need to deep dive into the data. Figure out what your audience cares about most. What websites are they on? What YouTube channels do they watch the most? What social media preferences do they have? What types of content are they sharing?
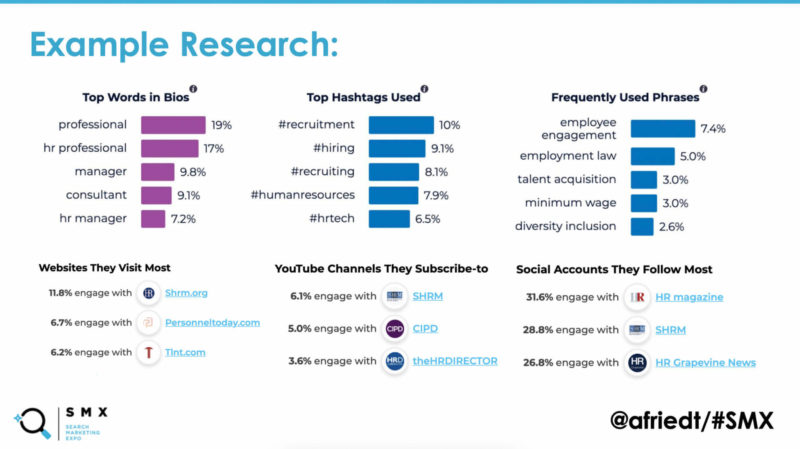
From there, Farley recommends noting the differences in this information between influencers. You may find some overlap, but the differences can help inform your strategy even more. In an example with an aerospace client, she found that the economic buyer’s second most-used social media channel was LinkedIn while the user buyer went to Instagram. This can change how you focus your campaign strategies and messaging for each platform.
The last part of the research is keyword and topic analysis. Any of the main keyword tools work for this part. “We look at — what are the key focus points? Is there any overlap? But also can I actually spot the buyer influencer” in what and how they’re searching, Farley said. This can craft how you’re displaying content and creating search ads or messaging landing pages. The key, she says, it tweaking the messaging for each product or service campaign to target those buyer personas.
Step 3. Other ways to use data and audience research. You can look at top channels for sponsorship opportunities like in podcasts or influencer campaigns that each buyer might listen to. You can target your media buys to these channels and even build relationships with hosts and reporters in these areas.
Implementing the research in PPC campaigns
Firstly, Farley recommends paid search advertisers think big and imagine what they would do if budget wasn’t a limiting factor.
Google Ads. “Go into each channel and create, cast, and layer. With Google, I like to use the custom audience or sandbox building of display campaigns. You can upload things like all of the YouTube channels that you found along with those key topic or purchase intents that you found in the keyword research to really get those estimates of: How many people are looking for this? And what could potential costs look like?” she added.
Farley also recommends layering custom with affinity or intent (especially if you have good lookalike or first part data) to see what works. You’ll have to balance what’s too narrow with what’s big enough to be able to serve. The key is understanding what’s possible and testing from there.
Microsoft Advertising. Microsoft’s Audience Network gets kudos from Farley, too. “You can actually target using LinkedIn data into their display network, so things like job function, industry, company, in-market segments… you can build that all and get your estimates and figure out what could a potential budget or strategy look like,” she said.
Facebook and Instagram. While these options are constantly changing and evolving, Facebook and Instagram have allowed us to target by job type and interest, and use our first-party data.
Working within your budgets
Now that we’ve dreamed big and seen what’s possible, we have to work within the frameworks set by clients and stakeholders including budget and regulations, etc. Farley offers a planning framework where she starts off looking at who her primary audience should be. She determines if there are specific focus areas like industry or location. From there she finds the best channel based on the audience insights we gained earlier and keeps her KPIs in mind. Leverage the percent of potential investment based on those set KPIs.

It’s also critical to look at the content or pain point to determine what it means for your ad assets. “We can’t be everything to everyone all the time because we have to work in the budgets,” Farley reminds PPC marketers. She recommends looking at your media map as percent by channel by funnel: “If we can say, if search will need to be 50%, then display is 20% because we can’t be always on for everything.”
Seasonality. Don’t forget seasonal trends, reminds Farley. “It just gives us a high-level look at what the seasonality in each market tells us.” You can know the best times to leverage campaigns, know when competitors will be bumping up costs, and more.
Testing. Make sure your settings are limiting waste before you launch! “Once you launch, test, monitor, optimize, and test again,” she recommends. After that, you can remove low-performers and update creative, ads and messaging to better fit your target audience. And, of course, amplify your best strategies. The cycle is never-ending, though, as she recommends advertisers continue to test, log, optimize, and test again.
Top insights:
- Find your buyer influencers, then leverage into audience targeting for campaigns.
- Determine what’s possible and then laser-focus in, on what matters most with realistic investments.
- Test and optimize audience layering with creative performance. Report, optimize, evaluate for success and repeat.
